Garbage incinerators play a crucial role in managing municipal waste and reducing the environmental impact of landfill sites. However, the operation of these facilities comes with inherent risks, both for the environment and the safety of the workers involved. To address these concerns, strict safety measures and regulations are in place to govern the operation of garbage incinerators.
Personnel Training and Certification
To begin with, fundamental aspect of ensuring the safe operation of garbage incinerators is the proper training and certification of personnel. Operators and maintenance staff must undergo rigorous training programs to understand the intricacies of the equipment, waste materials, and emergency procedures.
Fire Prevention and Control
Furthermore, the risk of fires in garbage incinerators is a constant concern. To mitigate this, these facilities are equipped with fire detection systems and automatic extinguishing mechanisms. Regular fire drills and maintenance checks are essential for preparedness.
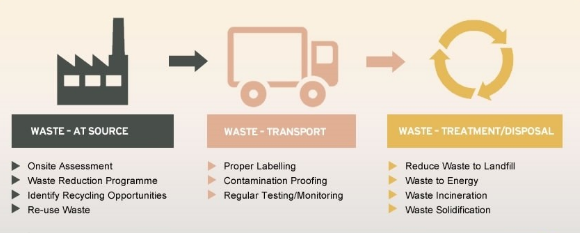
Emission Control
Moreover, stringent regulations are in place to limit harmful emissions from incinerators. Advanced filters and monitoring systems help reduce air pollutants, while routine emissions testing ensures compliance with environmental standards.
Waste Screening and Segregation
Effective waste screening and segregation are vital in preventing the introduction of hazardous or prohibited materials into incinerators. Therefore, strict protocols help ensure only authorized waste streams are processed.
Operational Protocols
Clearly defined operational protocols are established, specifying start-up and shutdown procedures, waste feeding rates, and temperature controls. In addition, adhering to these protocols is critical to prevent accidents.
Continuous Monitoring
Constant monitoring of incinerator performance is key to identifying issues promptly. Advanced sensors and control systems help operators keep a close eye on combustion efficiency and emissions.
Emergency Response Plans
Garbage incinerators must have comprehensive emergency response plans in place. These plans outline actions to be taken in case of fires, equipment failures, or any other potential incidents.
Occupational Safety Measures
Protecting the safety and health of incinerator workers is paramount. Personal protective equipment (PPE) is mandatory, and routine safety audits ensure a safe working environment.
Noise and Vibration Control
Garbage incinerators often produce noise and vibrations, which can affect nearby communities. Hence, regulations limit these impacts through noise barriers, vibration dampeners, and distance requirements.
Waste Transportation Safety
Waste transportation to incinerators is subject to strict regulations. Vehicles are required to adhere to safety standards, and drivers must undergo training in waste material handling to prevent spills and accidents.
Regulatory Oversight
Government agencies are responsible for overseeing incinerator operations and ensuring compliance with safety and environmental regulations. Regular inspections and reporting requirements help maintain transparency and accountability.
Public Awareness and Communication
Engaging with the community is essential for a successful garbage incinerator operation. Open and transparent communication about safety measures, environmental impact, and emergency procedures fosters trust and cooperation.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Before constructing a garbage incinerator, an environmental impact assessment is conducted to evaluate potential effects on the surrounding ecosystem. This ensures that the facility aligns with environmental regulations.
Waste-to-Energy Technologies
To improve safety and efficiency, many garbage incinerators now incorporate waste-to-energy technologies. These systems help reduce waste volume and generate energy from the incineration process.
Regular Audits and Upgrades
As technology and safety standards evolve, garbage incinerators require regular audits and upgrades to remain compliant and efficient. This includes updating equipment and controls.
Environmental Regulations
Stringent environmental regulations dictate emission limits and waste handling procedures. Operators must stay current with these laws to avoid fines and penalties.
Periodic Training and Refresher Courses
In addition to initial training, incinerator personnel should undergo periodic refresher courses to stay updated on safety practices and regulations.
Hazardous Waste Management
Moreover, incinerators that handle hazardous waste have additional safety requirements, including secure storage, strict disposal guidelines, and monitoring of waste streams.
Stakeholder Collaboration
Lastly, working in collaboration with government agencies, local communities, and environmental organizations is essential to ensure the continued safety and sustainability of garbage incinerator operations.
Conclusion
Garbage incinerators have evolved to become safer and more environmentally friendly facilities through the implementation of stringent safety measures and regulations. These measures, combined with technological advancements and community collaboration, help minimize the impact on the environment and ensure the well-being of both workers and nearby communities. Adherence to these regulations is essential in harnessing the benefits of waste-to-energy conversion while minimizing the associated risks.