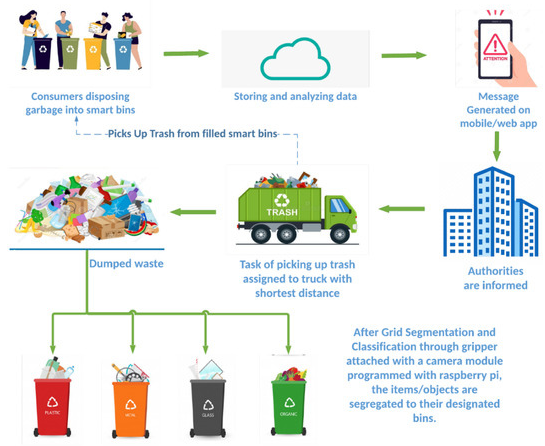
Every day, countless tons of garbage are generated by households, businesses, and industries around the world. But have you ever wondered what happens to all that waste after it’s collected? The process of managing and disposing of garbage is a complex and essential aspect of modern society. In this article, we will take a closer look at the journey of garbage after it’s taken from our homes and businesses, exploring the various stages it goes through to ensure proper waste management and environmental sustainability.
Collection and Transportation
Furthermore, the first step in the process begins with the collection of garbage from residential areas, commercial establishments, and industrial sites. Waste management companies utilize specialized trucks to gather the different types of waste, including organic, recyclable, and non-recyclable materials. These trucks transport the collected waste to local waste transfer stations or materials recovery facilities.
Sorting and Segregation
At the transfer stations or recovery facilities, the garbage is unloaded and undergoes a meticulous sorting and segregation process. Skilled workers and advanced machinery work hand in hand to separate recyclable materials like paper, cardboard, plastic, glass, and metals from non-recyclable waste. This separation is crucial as it allows for the effective recycling of materials, reducing the amount of waste that ends up in landfills.
Recycling
Recyclable materials that have been sorted are then sent to recycling plants. Here, the materials undergo further processing to be transformed into raw materials that can be used to create new products. For instance, paper and cardboard are pulped and turned into new paper products, while plastics are melted down and molded into new plastic items. Moreover, recycling not only conserves natural resources but also helps decrease the overall environmental impact of waste disposal.
Waste-to-Energy Conversion
Certain types of non-recyclable waste, known as waste-to-energy (WTE) feedstock, can be used for energy generation. These materials, which include plastics and other combustible items, are incinerated in controlled facilities to produce heat. This heat is then used to generate electricity through steam turbines. WTE facilities not only reduce the volume of waste destined for landfills but also contribute to renewable energy production.
Landfill Disposal
Despite efforts to reduce waste through recycling and energy recovery, some residual waste remains that cannot be effectively repurposed. This waste is transported to designated landfills for disposal. Modern landfills are designed with advanced engineering techniques to minimize environmental impact. They include features such as liners to prevent leachate (contaminated water) from seeping into the ground and systems to collect and treat methane gas, a byproduct of decomposing organic waste.
Composting
Organic waste, such as food scraps and yard trimmings, can be transformed through composting. Composting is a natural process where organic materials break down into nutrient-rich soil additives known as compost. This compost can be used to enrich soil in gardens, farms, and landscaping projects, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers and promoting sustainable agriculture.
Hazardous Waste Management
Certain types of waste, classified as hazardous due to their potential harm to human health and the environment, require special treatment. This includes items like batteries, electronic waste, and chemicals. Hazardous waste is collected separately and undergoes specialized processes to ensure safe disposal or treatment. Therefore, preventing the release of harmful substances into the environment.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the journey of garbage after it’s taken from our homes and businesses involves a series of intricate steps. These steps to ensure responsible waste management and environmental preservation. From collection and sorting to recycling and disposal, each stage plays a vital role in minimizing the impact of waste on our planet. As awareness about sustainable practices grows, more emphasis is being placed on reducing waste at the source, increasing recycling rates, and exploring innovative methods of waste-to-energy conversion.