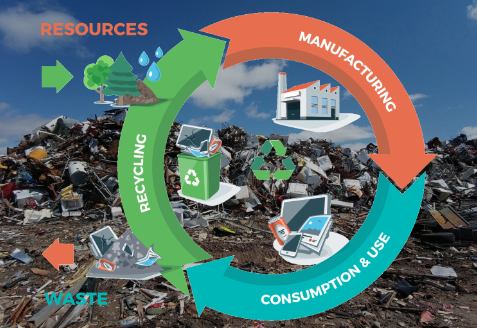
In a world grappling with environmental challenges, waste management has become a critical concern. The linear model of ‘take, make, dispose’ is no longer sustainable. Instead, the future of waste management lies in the principles of the circular economy, which emphasizes reducing, reusing, and recycling resources. This paradigm shift towards circular waste management systems is not just environmentally responsible but also economically viable.
The Linear vs. Circular Economy
The traditional linear economy is built on the idea of a one-way path for products: resources are extracted, products are manufactured, consumed, and then disposed of as waste. This approach has significant drawbacks, primarily the depletion of finite resources and the accumulation of waste in landfills and oceans.
Conversely, the circular economy presents an alternative model. It envisions resources flowing in a continuous loop, with minimal waste generation. In a circular system, products are designed with longevity in mind. Materials used in production are chosen for their recyclability. After the product’s useful life, materials are reclaimed and reused, reducing the need for virgin resources.
Reducing Waste Generation
Fundamentally, a circular waste management system involves waste prevention by reimagining product design, minimizing waste at the source. Achieving this entails utilizing durable materials, designing products for easy disassembly, and innovating packaging solutions that cut waste.
Furthermore, consumers hold a pivotal role as they adopt mindful consumption habits. Choosing long-lasting products and steering clear of single-use items practically reduces waste generation.
Reusing and Repurposing Resources
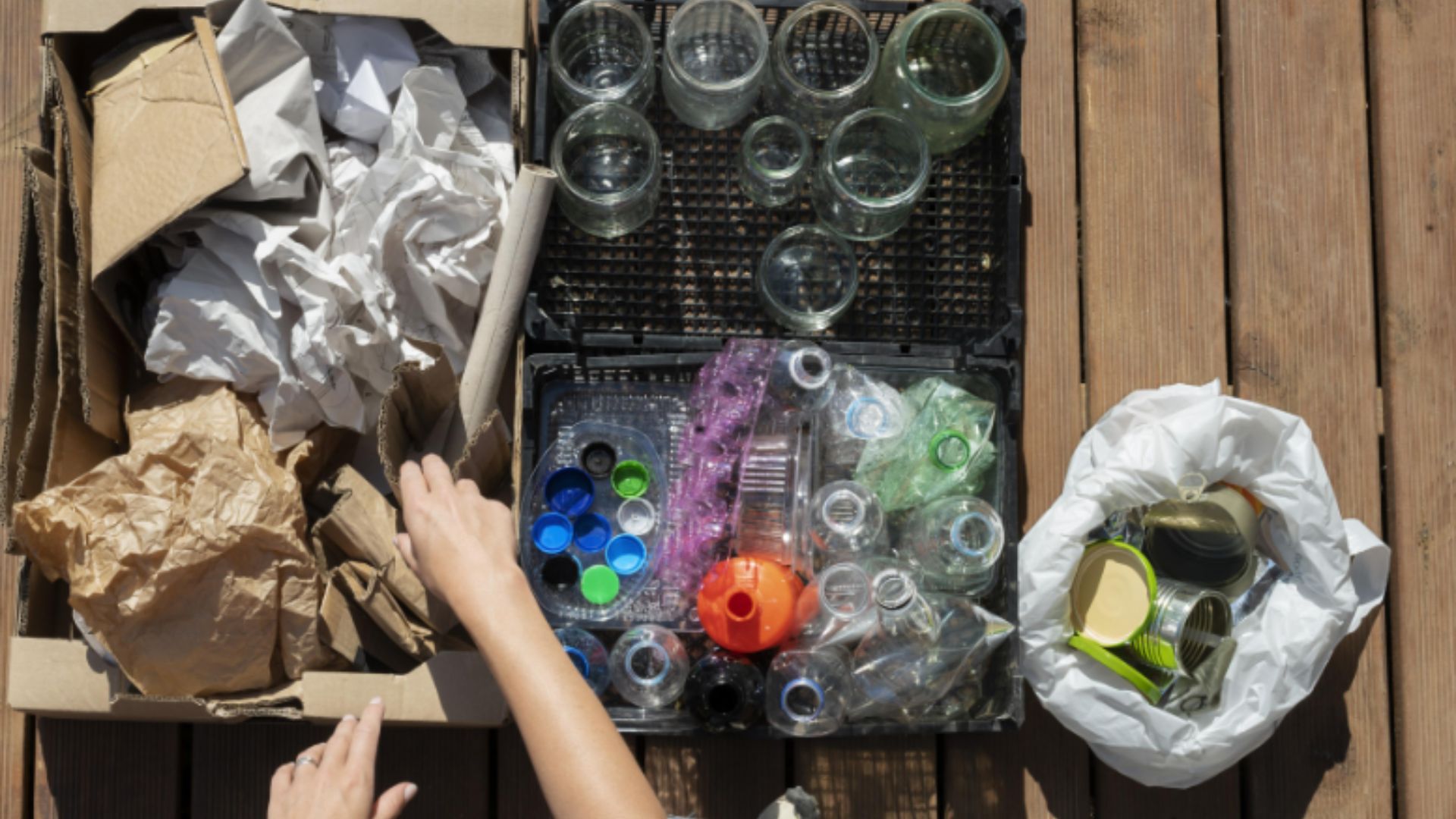
Circular waste management also places a strong emphasis on reusing products and resources. Instead of discarding items after their initial use, they can be refurbished, repaired, or repurposed. This not only extends the lifespan of products but also reduces the need for new manufacturing.
Take the example of the clothing industry, which is notorious for its environmental impact. In a circular economy, clothing can be designed for disassembly, making it easier to repair or recycle. Thrift stores and online platforms for selling used clothing have also gained popularity, promoting the reuse of fashion items.

Recycling as a Resource
Recycling is a cornerstone of circular waste management. Instead of letting materials go to waste, recycling facilities are essential for transforming used items into valuable resources. From paper and plastics to metals and electronics, recycling helps save energy, reduce the need for raw materials, and cut down on waste in landfills.
Furthermore, advancements in recycling technology have expanded the range of materials that can be effectively recycled. For instance, innovative processes can now recycle electronics, turning them into valuable secondary resources.
Economic Benefits of Circular Waste Management
One of the key advantages of adopting circular waste management systems is the potential for economic growth. Recycling industries, repair services, and resale markets create job opportunities and stimulate local economies. As the demand for sustainable products and services grows, businesses that embrace the circular economy can gain a competitive edge.
Moreover, reducing resource consumption through circular practices can lead to cost savings. Manufacturers can source recycled materials at a lower cost than virgin resources, making their products more affordable for consumers.
Challenges and Barriers
While the concept of circular waste management is promising, it is not without challenges. Transitioning from a linear to a circular economy requires significant investment in infrastructure, education, and technology. Governments, businesses, and consumers must work together to overcome these hurdles.
Consumer behavior is another obstacle. People often resist change, especially when it involves breaking away from convenient but unsustainable practices. Raising awareness and promoting the benefits of circular waste management is crucial for its widespread adoption.
Conclusion
The future of waste management systems is undeniably circular. The shift towards reducing, reusing, and recycling resources is no longer a choice but a necessity. Circular waste management not only preserves our environment but also stimulates economic growth, reduces resource depletion, and creates a more sustainable future for all.
It’s essential for individuals, businesses, and governments to recognize the importance of the circular economy and actively contribute to this transformative journey. By doing so, we can pave the way for a cleaner, greener, and more prosperous world.